CHRONIC SKIN DISEASES
- Eczema/ Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Acne
- Rosacea/ Acne Rosacea
INFECTIONS
- Bacterial Boils
- Fungal
- Ring worm
- Athlete's Foot
- Fungal Nail Infection
- Viral
- Chicken Pox
- Herpes Zoster
- Herpes Labialis
- Warts
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Urticaria/ Hives
- Itching
- Sunburn
- Rashes
SKIN DISCOLORATION
- Moles, Freckles
- Vitiligo
- Birthmarks
What is Eczema/ Dermatitis?
Its term for group of medical conditions that cause skin to become inflamed or irritated.
Most common type is Atopic eczema
Most of the people experience symptoms on and off throughout the life. The disease cannot be cured but can be controlled with proper treatment.
What are symptoms of Eczema?
- Itching
- Rash-commonly effects face, neck, back of knees and arms. Can spread to whole body.
- Skin becomes dry, thickened and scaly
- Pigmentation in dark skin type
What causes Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. It is thought to be an overactive response of the body's immune system to an irritant. It is this response that causes symptoms of eczema.
Commonly found in families with history of allergies or asthma.
How is Eczema treated?
Goal of treatment for eczema is to relieve and prevent itching.
- Lotions and creams to keep skin moist, these should be applied when the skin is damp.
- Cold compresses
- Topical steroid creams
- Oral steroids
- Phototherapy
How can eczema flares be prevented?
- Moisturize frequently
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature
- Avoid sweating
- Reduce stress
- Avoid wool
- Avoid harsh soaps and detergents
- Be aware of the foods that aggravate your problem
Quick facts about eczema
- Eczema is not contagious
- Eczema runs in families
- Eczema is not an allergic reaction.
Triggers in Eczema
Trigger does not cause eczema, but can make it worse.
- Wool
- Soaps and cleansers
- Makeup
- Dust and sand
- Irritants in environment
- Cold, flu
- Allergic reaction to mold, pollen
- Stress
- Hot showers
- Not using lubricant after bath
- Winter
What is Rosacea?
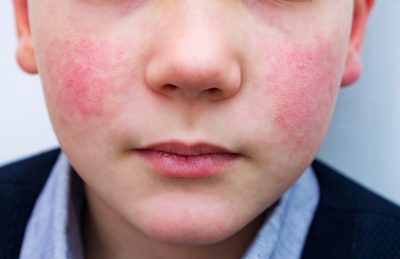
- Rosacea or acne rosacea is a chronic skin disease characterised by redness and pimple-like skin lesions over face.
- Rosacea effects central face- cheeks, nose and forehead.
- It causes Blushing of face, spider-like blood vessels on the face and burning or stinging feeling.
Trigger factors for Acne Rosacea
- Exposure to temperature extremes
- Strenuous exercise
- Sun exposure
- Stress, anxiety
- Cold wind
- Moving to warm environment from cold one as heated shops and offices in winters
- Food and drinks
- Alcohol
- Hot Tea and Coffee- Caffeine rich
- Spicy food
- Red wine, Beer, Yogurt- Histamine rich
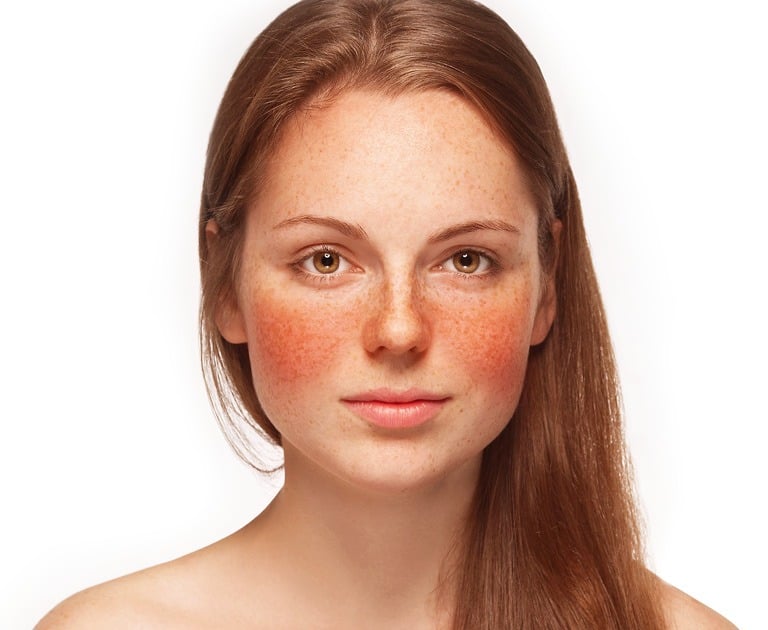

- Avoid sun exposure
- Use broad spectrum sunscreen
- Avoid activity in hot weather
- Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages
- Reduce stress
Facts about Rosacea
- Not contagious
- Chronic skin disease
- Rosacea cannot be cured, but it may be controlled with treatment.
When to see dermatologist of Rosacea/ Facial Redness?
Over-the-counter skin care products contain acids, alcohol and other irritants- that may worsen Rosacea.
If you feel persistent redness of your face, see your dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
WHAT IS FUNGAL INFECTION ?
- Tinea/ ringworm infection
- Candida Infection
- Pityriasis Versicolor
Tinea/ Ringworm Fungal Infection
- Restrict to dead keratinised tissue
- Stratum corneum of epidermis- Skin fungus
- Fully keratinised hair shaft- Hair fungus
- Nail plate/bed- Nail fungus

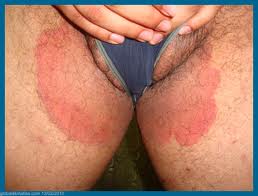
- Trunk and limbs
- Erythematous, scaly, circular lesions
- Sharply marginated with raised margin
- Central resolution is common
- Less inflammatory
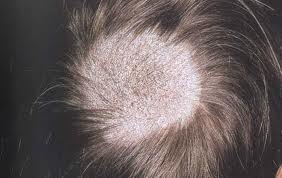
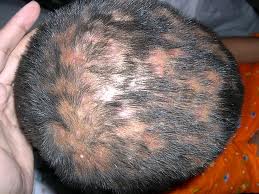
Tinea capitis
- Scalp fungal infection
- Predominantly children
- Adults with AIDS
Symptoms of scalp fungal infection
- Gray patch- scaling with patchy hair loss
- Black dot- formation of black dots as the affected hair breaks at the surface of scalp
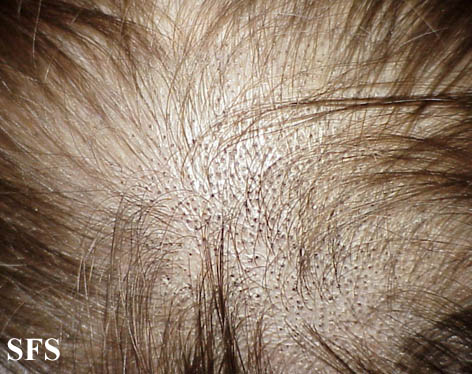
- Diffuse pustular- scattered pustules
- Kerion- most severe, painful inflammatory mass with loose hair
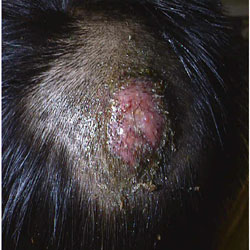
Scalp Fungal infection cure
Kerion
- Removal of crusts- wet compresses
- Coexistent bacterial infection must be treated
- Oral steroid can be used early in treatment course
Tinea barbae
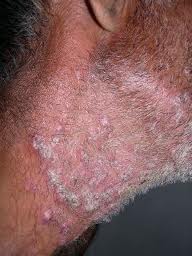
- Fungal infection of beard and moustache
- Highly inflammatory pustular folliculitis, exudation and crusting
- Dry, reddish, scaly lesions enclosing lustreless hair stumps
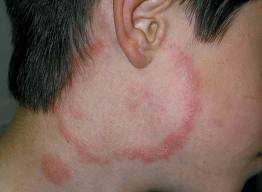
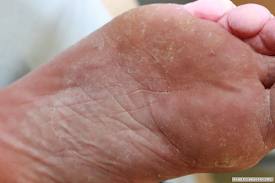
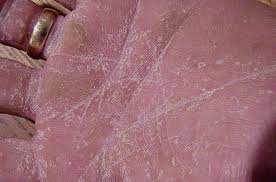
Tinea pedis/ Foot fungus
Symptoms of foot fungus
- Intertriginous dermatitis- peeling, maceration and fissuring affecting lateral toe clefts
- Scaling hyperkeratotic variety- Dry type infection
Skin fungal infection of Groin
Steroid-modified tinea/ Tinea incognito
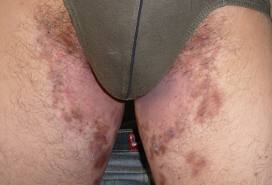
- Oral or topical steroid
- Clinical picture altered
- Raised margin diminished
- Scaling lost
- Nodules
- Bruise-like brown discoloration
Fungal nail infection/ Onychomycosis
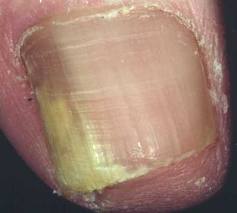
Nail fungus symptoms
- Streak or patch of discoloration, white or yellow at the free edge of nail plate, often near lateral nail fold
- Dorsal surface of nail plate is eroded, well-circumscribed powdery white patches, away from free edge
Topical treatment for nail fungus
Avulsion of nail or removal of infected areas
What is Candidiasis ?
Candida Intertrigo
Avulsion of nail or removal of infected areas
What is Candidiasis ?
Candida Intertrigo

- Infectious/non-infectious inflammatory condition of two closely opposed skin surfaces
- Under arms, groin, infra mammary, inter-digital
Risk factors for candidia yeast infection
- warm, humid environment
- Obesity
- Tight clothing
Candida infection symptoms
- Soreness and itching
- Erythema, moist exudation
- Spreads with fringed, irregular edge and tiny erosions
- Papular or pustular satellite lesions are classical
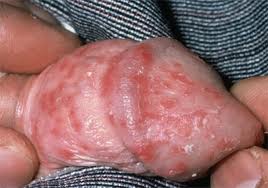
Candidal balanitis
Risk Factors
- Uncircumcised men
- Abundant vaginal candida carriage or frank vulvovaginitis in sexual partner
- Corticosteroid use
- Immunocompromised
- Poorly controlled daibetes
Clinical features

- Tiny papules or pustules develop on glans a few hours after intercourse
- Rupture leaving a peeling edge
Candidal Paronychia
Clinical features
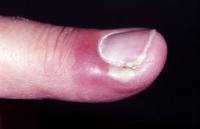
- Nail fold red and swollen
- Loss of cuticle
- Thick white pus may discharge
- Nail dystrophy
What is tinea versicolor?
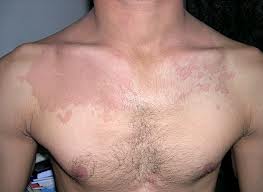
- caused by lipophilic yeast Malassezia, normal flora of skin
- Warm climate
- Family history
- Rare in children, more common in late teens and early twenties
Tinea versicolor symptoms
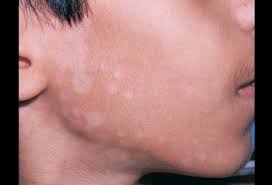
- Patient usually complains of patchy change of skin color, white patches
- Asymptomatic
- Red, brown, hypopigmented macules or patches
- Fine, branny scaling
- Upper trunk, upper arms, neck and abdomen